Magnesium
A mineral involved in millions of the processes of the human body, is important
for brain function and heart health is a well-known product called Magnesium.
This multi-talented mineral may help quiet the mind and body, making it easier to
fall asleep.
Through studies, people have found that magnesium’s relaxing effect
could be partly due to its ability to regulate the production of melatonin, a
hormone that guides your body’s sleep-wake cycle.
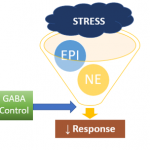
Magnesium also appears to increase brain levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a brain messenger with
calming effects.
Magnesium Studies
Studies report that insufficient levels of magnesium in your body
may be linked to troubled sleep and insomnia.
On the other hand, increasing your magnesium intake by taking supplements may help you optimize the quality and
quantity of your sleep.
One study gave 46 participants 500 mg of magnesium or a placebo daily for eight weeks.
Those in the magnesium group benefited from overall better sleep quality.
So, this group also had levels of melatonin and renin at a much higher level; both
hormones that will regulate your sleep.
Another small study shows that their participants must be given a supplement that holds two hundred and five
milligrams of magnesium slept way much better than the participants who were given placebo pills.
The supplement, Magnesium, also contained five milligrams of melatonin and eleven milligrams of zinc; this made it difficult to
decipher the effect of the Magnesium making it difficult to attribute the effect to magnesium
alone.
It’s worth noting that both studies were performed on elderly adults, who
may have had lower blood magnesium levels to start with.
It’s uncertain whether these effects would be as strong in individuals with a good dietary magnesium
intake.
Magnesium can improve the quality of your sleep!
Bottom line, Magnesium has a relaxing effect on the body and brain,
which quite possibly could help improve the quality of your sleep.
“The Institute of Medicine suggests a daily dietary intake of 310–360 mg of
magnesium for adult women and 400–420 mg for adult men (1).
Foods that contains magnesium…
You can get magnesium through drinking water and eating foods such as green vegetables,
nuts, cereals, meat, fish and fruit (1).
Very few studies have directly tested the effect of magnesium supplements on insomnia, making it hard to recommend
specific amounts.
However, the aforementioned clinical trials used amounts in the
range of 225–500 mg.
The upper limit considered safe from supplements is actually 350 mg per day, so avoid trying this higher dose without medical
supervision (2).
Since it’s clear that magnesium deficiency can affect sleep, a good first step is to make sure you’re getting adequate amounts from whole
foods” – https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/magnesium-and- sleep#section6.